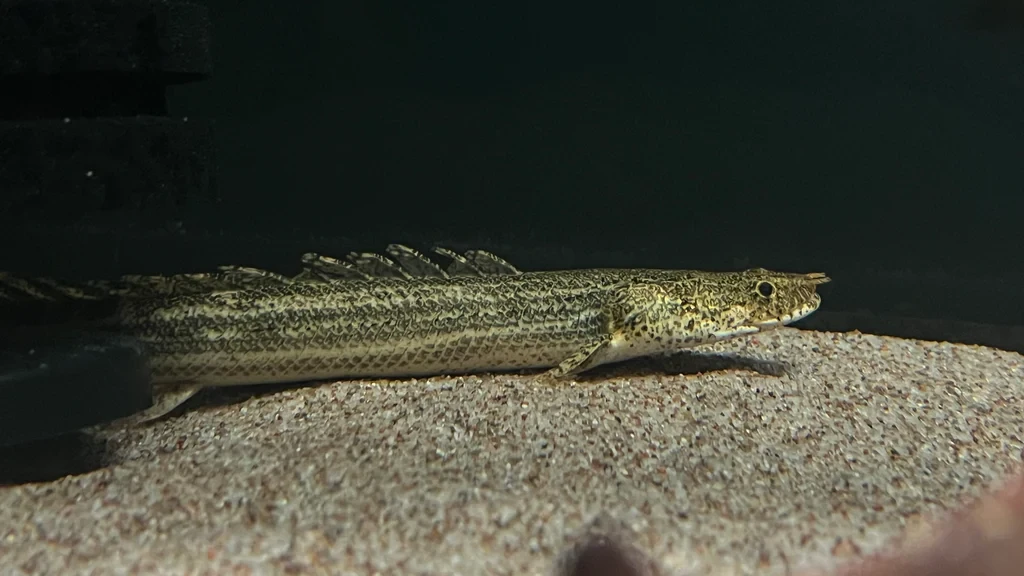
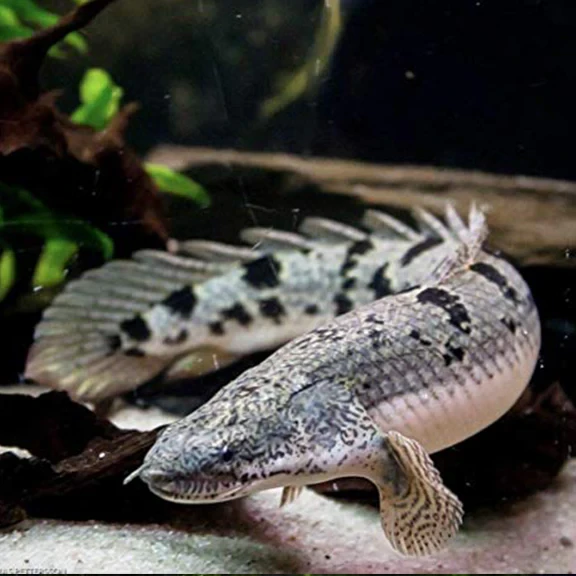
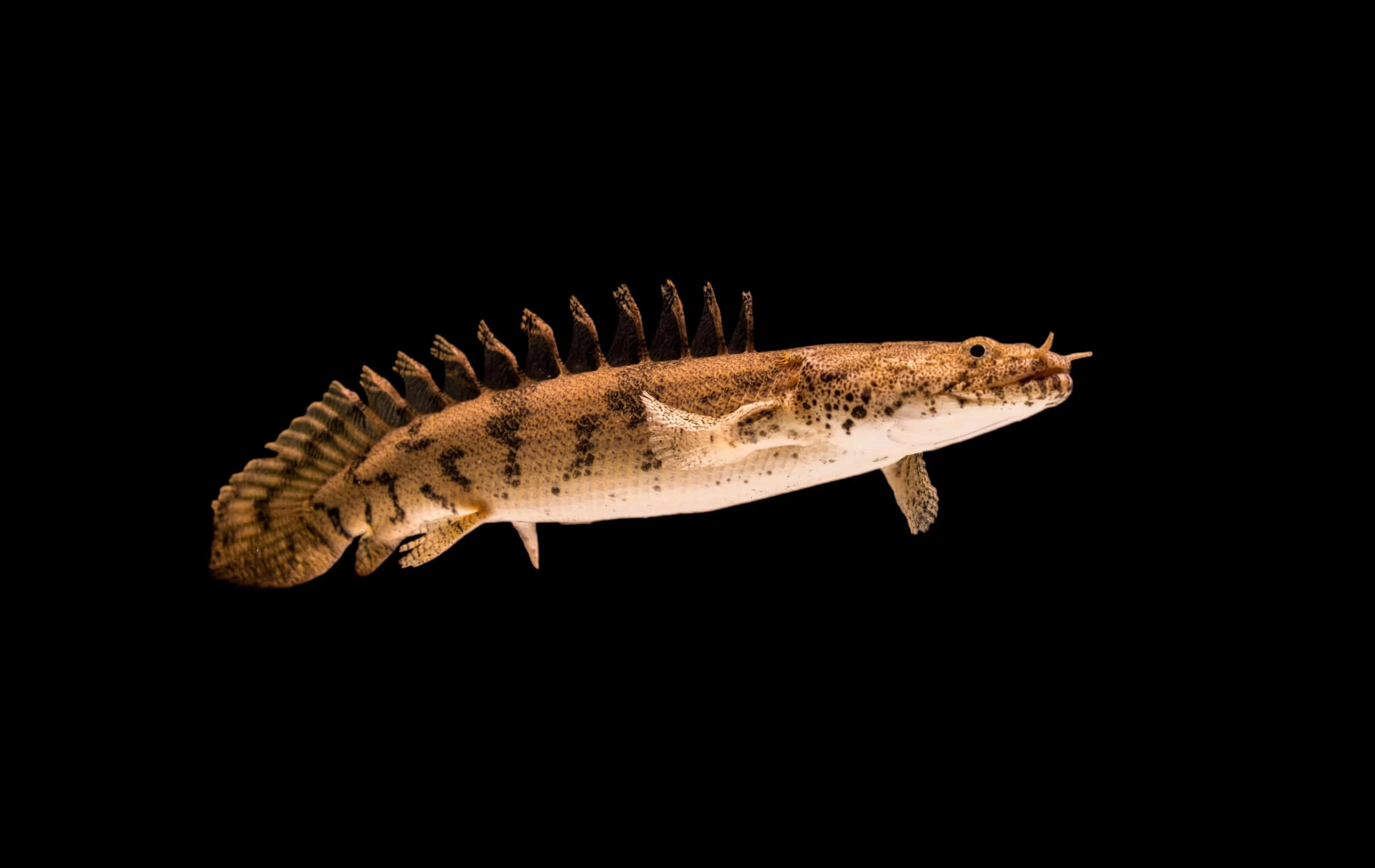
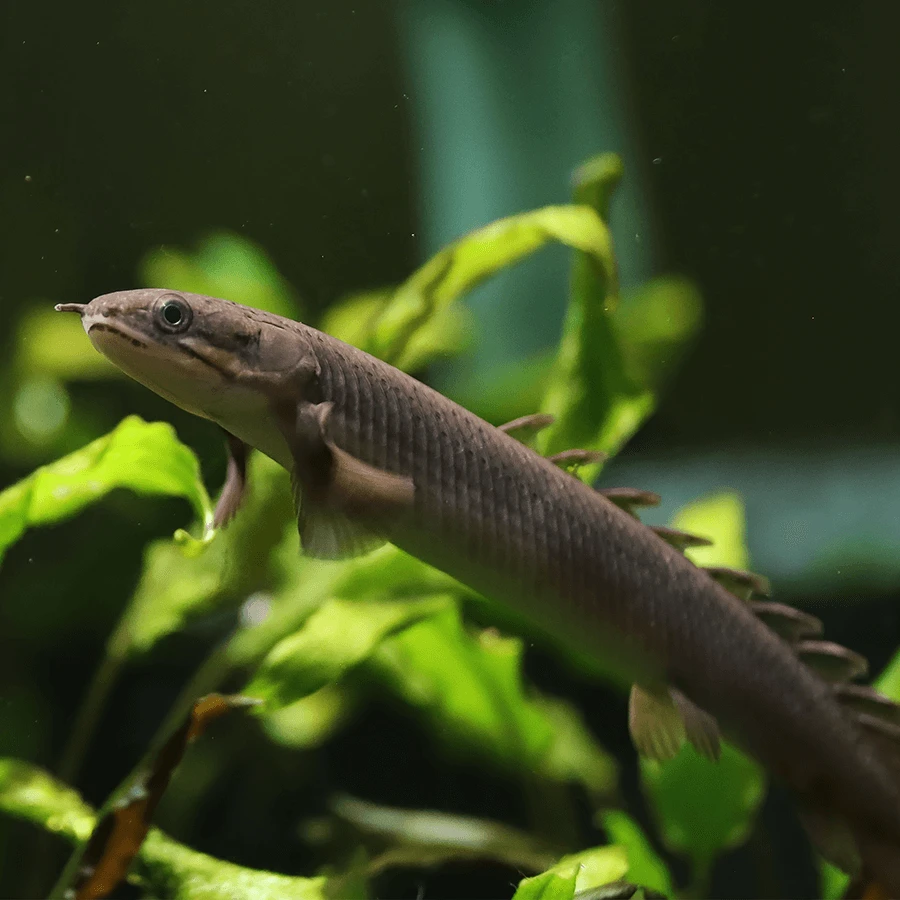
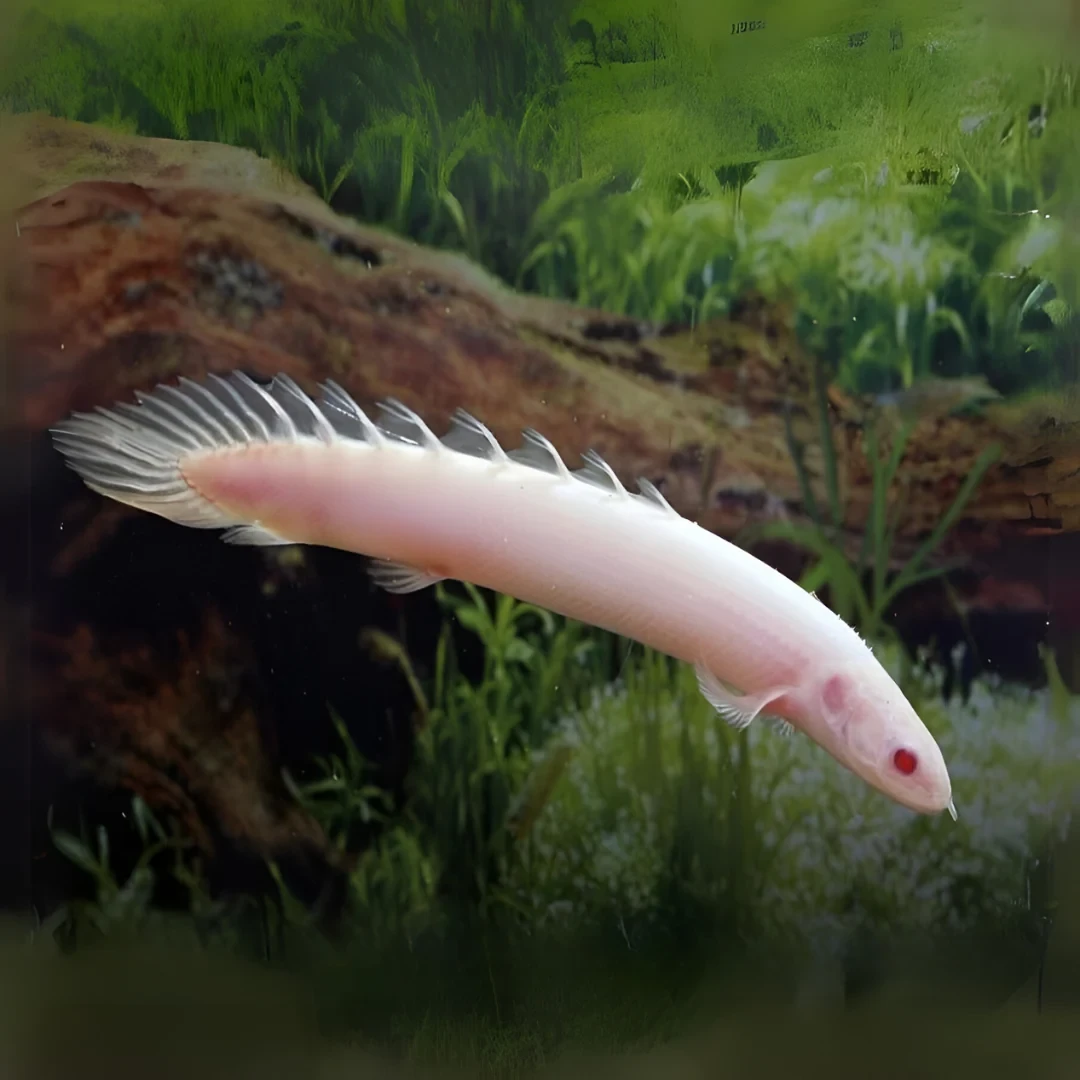
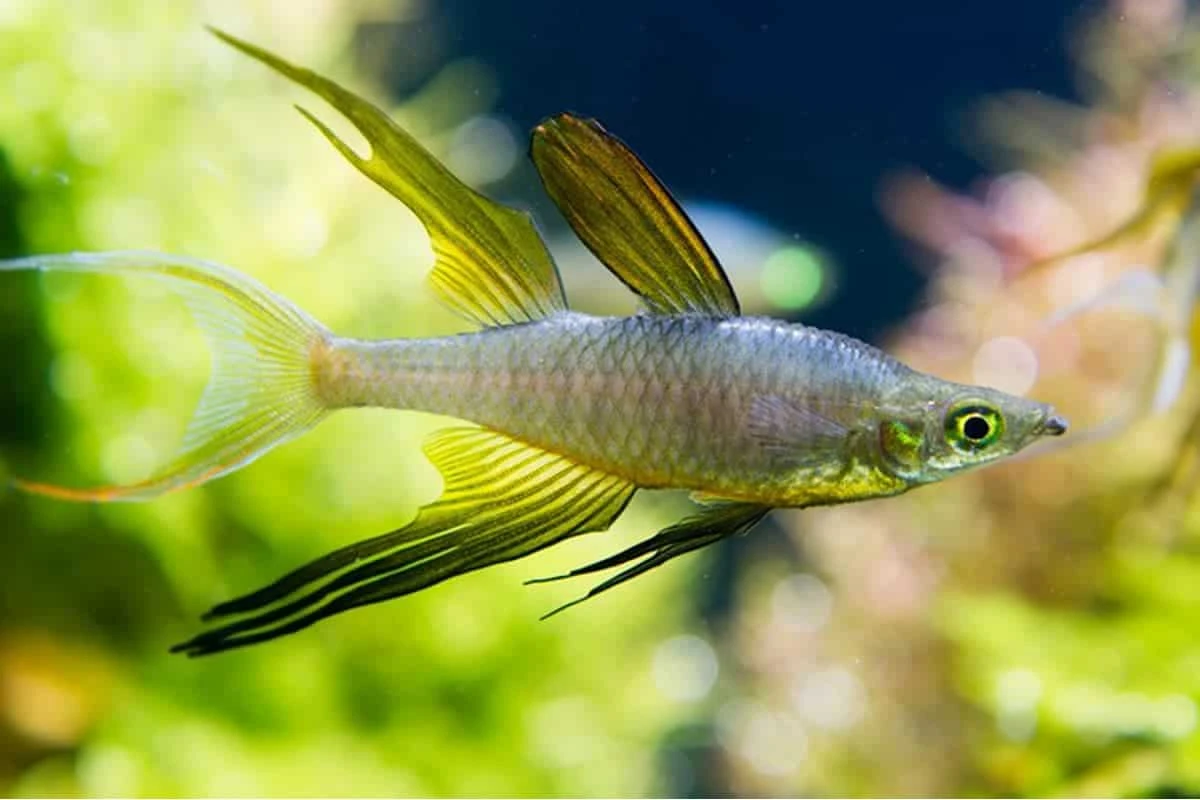
The Lapradei Bichir (Polypterus bichir lapradei), also known as the Laprade Bichir, is one of the largest bichir species. It has an elongated body with a prehistoric appearance and is known for its powerful predatory instincts.
Key Information
• Maximum Size: Can grow up to 24-30 inches (60-75 cm) in captivity, with wild specimens occasionally exceeding this size.
• Native Habitat: Found in West and Central Africa, particularly in the Nile River, Chad Basin, and other freshwater bodies. It prefers slow-moving or stagnant waters with muddy or sandy substrates.
• Growth Rate: Moderate; juveniles grow quickly in the first year but slow down as they mature.
• Lifespan: 15-25 years, with proper care and diet.
• Diet: Carnivorous – primarily feeds on fish, crustaceans, insects, and worms in the wild. In captivity, they accept live foods, frozen foods (such as shrimp, bloodworms, and fish fillets), and high-protein sinking pellets.
• Breeding Season: Rare in captivity but occurs in the rainy season in the wild. Males fertilize eggs scattered by the female among plants.
• Best Tank Mates: Lapradei Bichirs are large and predatory, so they should be housed with other large, peaceful but robust fish. Good tank mates include:
• Other large bichirs
• Arowanas
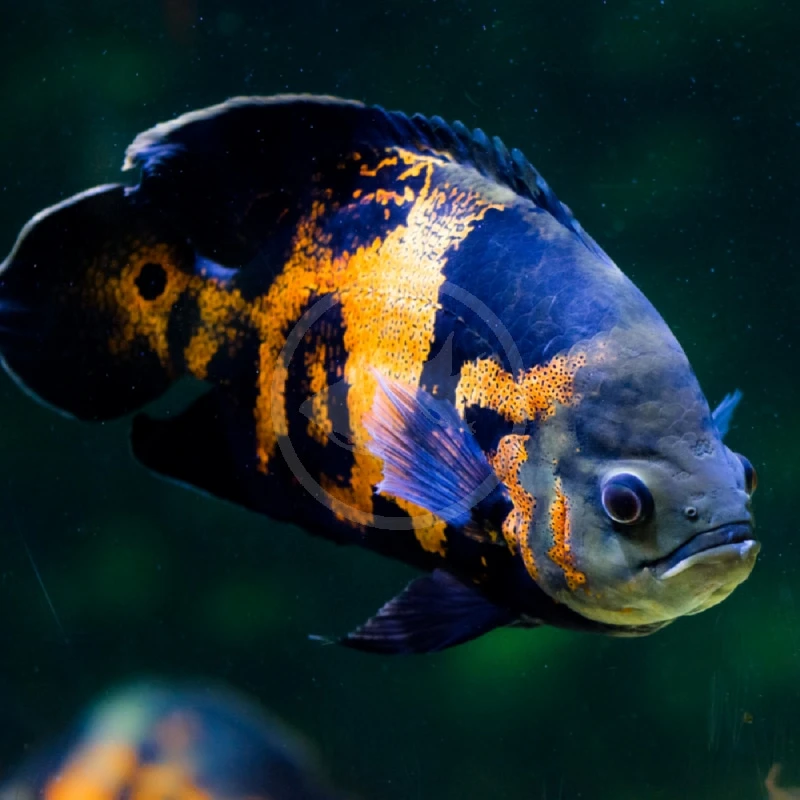
• Large cichlids (such as Oscars, Peacock Bass, or Jaguar Cichlids)
• Large catfish (such as Synodontis, plecos, or Tiger Shovelnose)
• Stingrays (if tank size allows)
• Silver dollars
Tank Mate Considerations
• Avoid small fish, as they will be eaten.
• Avoid aggressive or fin-nipping fish, as they may harass the bichir.
• Ensure tank mates are large enough not to be seen as food but not aggressive enough to stress the bichir.